E-learning Role Play: Definition, Stakes, and Educational Value
For a training manager, instructional designer, or HR director, the question is no longer “Should training be digitized?” but “How can training be made effective, engaging, and applicable on the job?” E-learning role plays address this very issue. They are interactive, believable scenarios that place the learner in a realistic context close to their daily routine, allowing them to learn by doing and deciding. These include simulations, digital role-playing, or serious games where the user explores, chooses, sees the impact of their actions, and receives immediate feedback. The educational promise is twofold: develop operational skills (procedures, diagnostics, safety) and behavioral skills (communication, leadership, ethics) in a safe, replayable, and measurable environment.
This format has become essential because it meets the criteria of modern training: authentic interactivity, personalization through conditional logic, gamification to boost motivation, and full trackability within a LMS. More importantly, no-code authoring tools like VTS Editor allow for the creation of advanced experiences without coding, significantly reducing production time.
Formats and Fundamentals of E-learning Role Plays
What is a Role Play in Digital Training?
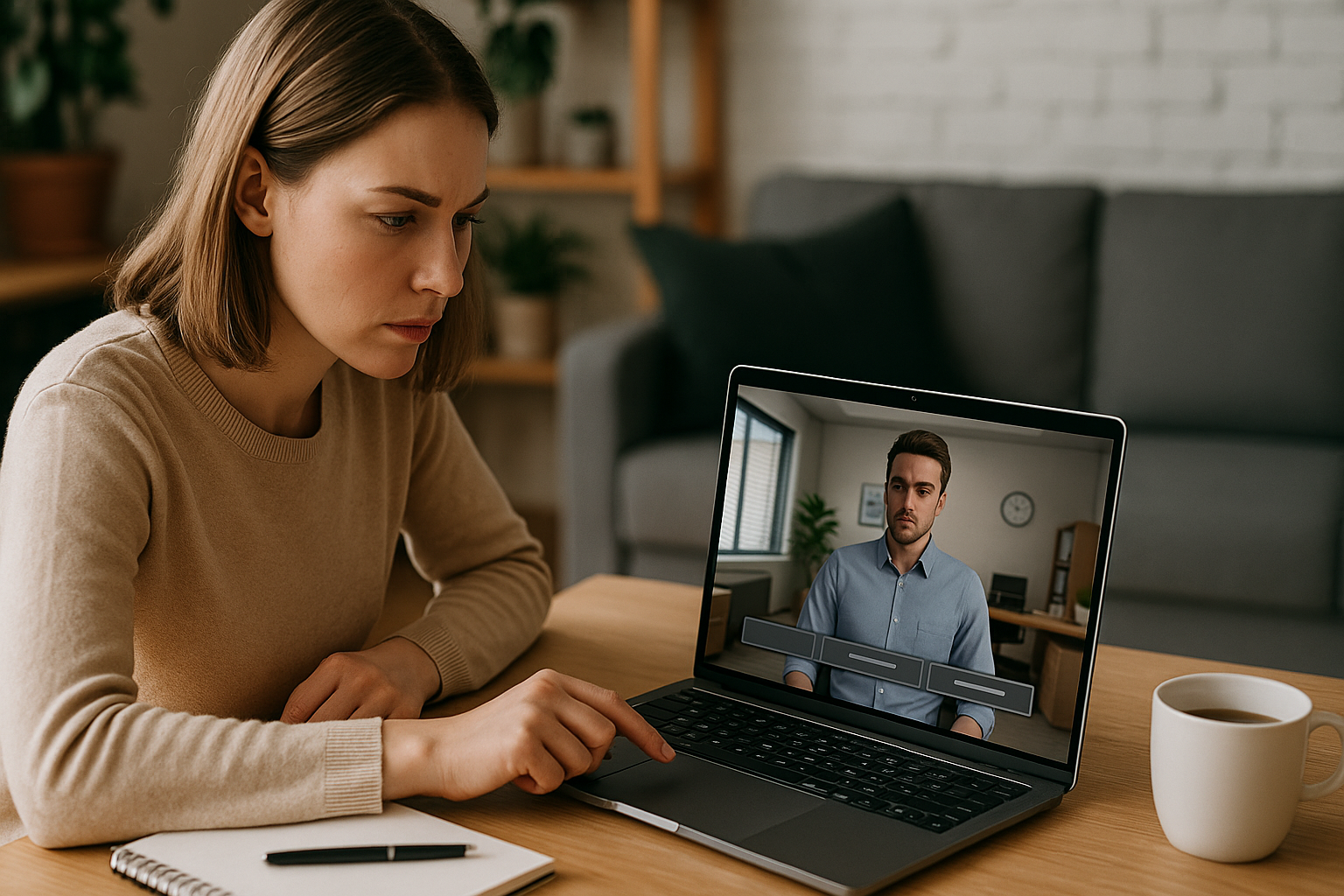
In practical terms, a digital role play recreates a professional context with realistic stakes, characters, visual cues, and decisions to make. The learner is no mere spectator: they take on a role, speak, observe, choose, and act within an environment, then see the consequences of their actions. From the HR/Training perspective, the benefit is clear: confront employees with the “moments that matter” in the job — without real risk but with enough realism to create practical field benchmarks.
Simple example: a manager needs to address a performance issue with an employee. In a role play, the manager (learner) receives context, selects their words, manages the simulated colleague’s emotions, and adjusts listening. Based on these choices, the digital character reacts, the atmosphere shifts, visual clues appear, and a competency score (active listening, assertiveness, clarity) adjusts. The trial-and-error loop is immediate: you see what works, try again differently, and improve.
Role Play, Simulation, Case Study, Serious Game: Know the Differences
These terms are often confused:
- Case Study: analysis of a described situation, limited interactivity.
- Simulation: faithful reproduction of a system, process, or gesture (maintenance, safety, compliance).
- Role Play: decisions in context, visible consequences, immediate feedback.
- Serious Game: same foundation with visible game-like mechanics (challenges, badges, levels).
In practice, an effective module combines these approaches: short storytelling for context, a procedural segment to anchor key steps, multiple-choice dialogue to train attitudes, rich feedback, and a splash of gamification to sustain engagement.
Instructional Design Principles That Make the Difference
Kolb’s experiential learning model comes naturally into play: live a situation, reflect on the outcome, formalize best practices, try again. Well-designed multimedia learning enhances memorization by combining words, images, and sounds in a complementary manner (see Mayer, 2009). Quick, contextual feedback helps optimize learning and strategy adjustment (see Roediger & Karpicke, 2006). Spaced repetition and replayability — supported by nonlinear storytelling and controlled randomness — foster long-term retention (see Cepeda et al., 2008).
Non-linearity is not a gimmick — it drives engagement. It relies on a clear logic (branches, flags, variables, score thresholds) to personalize the experience. Example: if the learner overlooks a key clue, a flag is triggered, and the narrative diverges (remediation, additional hint, or increased difficulty). This structured adaptivity, though invisible to the user, brings the experience closer to reality, where each decision creates new constraints.
Examples of Business Applications
Use cases are numerous and compelling:
- Onboarding: culture, key procedures, safety habits.
- Customer Relations: listening, rephrasing, objection handling with realistic personas.
- Management: delegation, feedback, mediation in a secure environment.
- Compliance (GDPR, EHS, anti-corruption): dilemmas, proof of understanding.
- Production/Quality: standards, tasks, checks and diagnostics.
Discover real-life results in our client case studies (cybersecurity, field safety, onboarding, sales, healthcare, etc.).
Why Use E-learning Role Plays? Educational and Business Benefits
Engagement, Focus, and Retention
Making decisions, observing consequences, and receiving immediate feedback captures attention far better than passive learning. Skilled use of media (voice, images, videos, sound effects) multiplies encoding channels and boosts retention (see Mayer, 2009). Active, interactive tasks promote deep learning (see Chi, 2009).
Fast Transfer to the Job
Role plays are pragmatic — they prepare users for real decisions and actions. A technician diagnoses a breakdown by following a process; a customer advisor handles an unhappy client without escalation risk; a manager chooses the right words in a sensitive conversation. The gap between training and work narrows, accelerating skill acquisition and reducing field errors. Simulation-based approaches are well-supported by research, especially in healthcare (see Cook et al., 2011).
Measuring Impact and Driving Performance
In an LMS, a SCORM-exported module reports on progress, score, pass/fail status, time spent, and number of attempts. Even better, a competency-based framework (communication, problem-solving, safety, etc.) allows for a detailed view of strengths and areas for improvement. You can set thresholds (e.g., “pass if score > 80% and critical step is validated”), trigger targeted remediation, and issue badges for milestones. Data becomes a real strategic HR tool.
Scalability and ROI
A well-designed e-learning role play is reusable, adaptable, and translatable. Targeted updates (dialogues, prompts, media) don’t require redoing the entire module. Classroom training costs fall, onboarding time is reduced, risk diminishes, and quality improves. In short: learning ROI and business ROI go hand in hand.
Designing an Effective E-learning Role Play: Method and Tools
Start with Objectives and Indicators
Begin with the target competencies and observable behaviors: what should be seen or heard in a standard situation? Define success criteria (score thresholds, critical errors, time constraints if needed). Decide which data is reported to the LMS: progress, status, total score, breakdown per competency, number of attempts. This initial clarity informs the entire scenario.
Write a Believable, Impactful Scenario
Design personas (impatient client, struggling employee, demanding auditor) and a credible context (locations, vocabulary, constraints). Authentic dialogue makes all the difference: a managerial conversation sounds right if the wording is nuanced and body language (eye contact, emotions, gestures) matches the tone. Offer real choices: three plausible options — one appropriate, one debatable, and one risky. Feedback should explain the reasoning, offer a hint or resource, and show the character’s reaction. Vary the rhythm: tense moments, breathing spaces, micro-briefings.
Multimodality, Accessibility, and Immersion
Sound and voice bring the experience to life: a well-chosen synthetic voice (or imported audio) sets the tone; ambient sound places the action; a short video explains a process; a foreground visual displays a key message at the right moment. Think accessibility: clear subtitles, contrast control, concise text, alternatives to media when needed.
Adaptive Logic and Non-linearity
An effective role play is both demanding and supportive. Branches must be controlled: if a learner makes several risky decisions, trigger contextual remediation; if they succeed, slightly increase complexity or offer an alternative case to reinforce learning. Variables and flags retain states (accessed resources, found clues, validated steps). Competency-based scoring personalizes progression (“Continue” if > 75%, “Reinforce” otherwise). Randomization (question order, case variants, changing media) supports replayability without compromising the goal.
Prototype, Test, Iterate
Aim for a playable MVP fast. Test with 3 to 5 target users: observe understanding of instructions, navigation, hesitation points, time, and drop-off points. Use analytics (success rate, frequently chosen paths, time spent) to adjust. Iterate in quick cycles: rephrase directions, rebalance options, tweak timing, or trim heavy media.
Technical Integration and Deployment
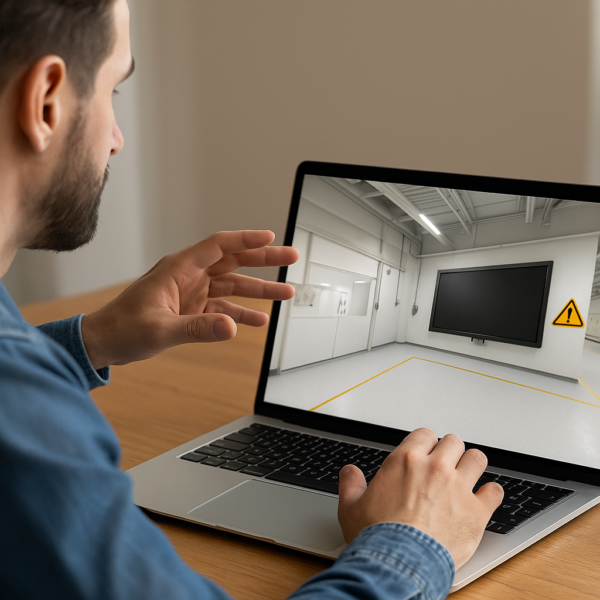
Before SCORM export, lock completion policies (criteria, resumption) and data granularity. Test on real devices (PC, tablet, mobile), optimize media (file size, format), and anticipate network constraints. In 360° or VR setups, alternate guided moments (fixed then directed camera) and free exploration to channel attention without causing frustration.
VTS Editor: The Tool to Build Your E-learning Role Plays Without Coding
VTS Editor is designed for this approach, with a block-based visual interface to build non-linear scenarios by linking scenes, interactions, and logics. A training manager can assemble without programming. An instructional designer finds their landmarks: goals, feedback, assessment, and pacing.
Example flow: start with a title animation and brief context, follow with a slideshow, then place the learner face-to-face with a character. The blocks “Talk,” “Emotion,” “Character Animation,” and “Gaze” make the exchanges credible, with subtitles, history, and optionally a synthetic voice. Decisions use “Dialogue Choices” or “Quiz” blocks depending on the goal, with competency scoring and contextual feedback. The logic uses “Flags”/“Check Flag”, “Score”/“Check Score”, and “Counter” to limit attempts, “Random” and “Sequence” to vary scenarios. Attention is guided via “Media in Scenery” for visual cues, “Foreground” for alerts, and “Show Interface” to highlight score or time when time-limited via “Countdown.” For motivation, the “Badge” block rewards milestones and syncs with VTS Perform if used. Finally, “Progression” sets percent, status, and overall score prior to SCORM export.
For advanced needs: launch a resource at the right time (“Open Resource”), connect to an API (“Web Request”), or use a virtual coach (“AI Request”). “Variables” and “Variable Media” personalize content and randomize visuals without multiplying blocks, streamlining maintenance. In 360° environments, “Freeze 360” and “Force 360” effectively control the camera.
Two best practices to remember:
- Think in “chapters” and resumption points, especially for field teams with limited time. VTS Editor allows you to teleport learners exactly back to where they left off — no loss of context or score.
- Plan measurement from the outset: identify target competencies, configure scores and conditions, and instruct managers on how to interpret the results. The easier the reporting, the more effective the support. For further insights, consult our white paper The Benefits of Digital Learning Simulation.
Going Further with E-learning Role Plays
To transform declarative knowledge into operational know‑how, e-learning role plays are a powerful lever. They turn the learner into an actor, transform mistakes into learnings, speed up transfer to the job, and deliver measurable data to track progress. With a no-code authoring tool like VTS Editor, you can quickly build immersive, non-linear, scenario-driven experiences including dialogue, feedback, competency-based scoring, badges, contextual resources, and SCORM export.
The best starting point is a short, high-priority use case (onboarding, customer relations, management, safety). Prototype in a few days, test with a representative audience, measure, and iterate — it becomes a repeatable model. Let yourself be inspired by our client case studies and already deployed interactive role plays. Ready to take action? Request your free trial from the “Try Virtual Training Suite” page and experience the power of a well-designed e-learning role play.
Join the Community
Explore our full offering on the Serious Factory website and equip your teams to create, deploy, and measure experiences that drive behavioral change.
Explore our exclusive resource on educational role-play scenarios: learn how to define, design, and deploy your programs to maximize the impact of your training.
👉 Access the content