Training Escape Games: A Lever Against Attention Deficit
In a context where teams are highly solicited and mental workload is increasing, the training escape game stands out as a format that combines engagement, lasting memorization, and impact measurement. It transposes the mechanics of escape games (riddles, searches, codes, cooperation, time constraints) into a structured, competency-oriented learning system. Whether in-person, remote, synchronous or asynchronous, it creates a mission-based experience that motivates learners to learn and perform. Research has shown that well-designed games promote engagement and a state of flow conducive to learning (Hamari et al., 2016), and that clear design helps manage cognitive load (Sweller, 2011).
Beyond Gaming: A Results-Oriented Learning Experience
A pedagogical escape game is a scenario-based experience composed of riddles and decision-making, aligned with clear learning objectives. The learner is immersed in a mission with constraints (time, limited resources, critical errors), interactions (clues, manipulations, choices), and immediate feedback. Unlike a simple quiz, the narrative, cooperation, and exploration are central: we learn by doing, testing hypotheses, and adjusting strategy. For L&D managers, instructional designers, and HR professionals, this is an ideal format to develop knowledge (compliance, products), know-how (procedures), and soft skills (communication, leadership, stress management). To explore more on active learning, see Learning by Doing.
Essential Principles and Business Use Cases
A Scripted Learning Experience, Not Just Entertainment
- Objectives and Success Criteria: What skills are being observed (customer communication, procedural application, detection of weak signals) and what indicators are being tracked (overall and skill-specific scores, time, critical errors, hints used)?
- Narrative Arc: A credible mission that brings meaning (e.g., solving a security incident before a regulatory deadline, saving a key client).
- Collaboration: Roles, active listening, information sharing; the assessment covers both cooperation and the final solution.
- Constraints: Timer, limited resources, branches leading to real choices, optional clues to prevent dead ends.
- Feedback and Debrief: Immediate reactions and guided debriefs to turn performance into transferable learning for the job.
Design with VTS Editor (No-Code Authoring Tool)
Create rich, measurable scenarios without coding using VTS Editor:
- Measurement and Monitoring: Score and Check Score blocks for success thresholds; Progress for module status; SCORM export; consolidated analytics via VTS Perform; LMS integration.
- Dynamic Storytelling: Speak (dialogues), Emotion and Character Animation, Eye Contact, Sound (ambience), Video and Slideshow.
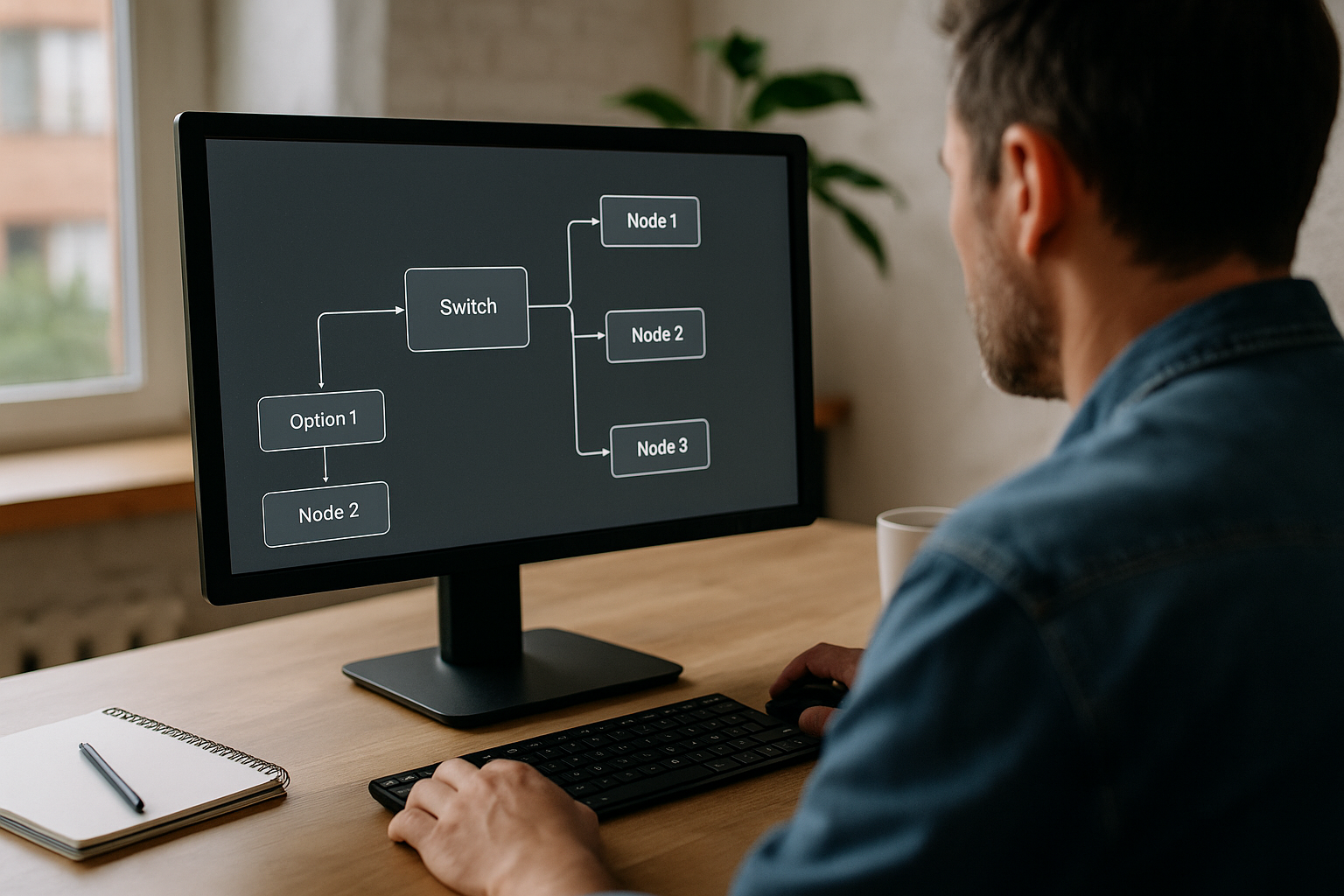
- Constraints and Pace: Countdown, Wait, Random/Switch/Sequence, Counter (limit attempts).
- Interactive Feedback: Message, Quiz/Multiple Choice/True-False/Text-Numeric Input/Numeric Keypad/Slider, Badge.
- Exploration: Clickable zones, Decor interaction, Media in Decor, Foreground.
Flexible Formats: In-Person, Remote, Phygital, 2D/3D/360°, Synchronous/Asynchronous
In-person sessions can mix physical clues (cards, labels) and digital interface for a phygital effect. In remote synchronous sessions, host virtual classes in teams with screen sharing; in asynchronous mode, make a mission available for a defined period. 360° environments enhance immersion: Freeze 360 to lock attention during briefings, Force 360 to direct the camera to a clue, then enable free exploration.
Professional Use Cases
- Onboarding: “Unlock” departments (IT, HR, Finance) through mini-puzzles about processes and values; each win unlocks a useful resource.
- Compliance/HSE/GDPR: Simulate a surprise audit or data breach; decisions under a timer; risk-focused debrief.
- Sales and Customer Relationships: Lead qualification/prioritization, objection handling; branched dialogues and skill-based scoring.
- Cybersecurity: Phishing detection, fake websites, 2FA codes; simulated consequences. See the Thales case.
- Management/Leadership: Delegation, feedback, conflict management; behavior observation; group debrief.
- CSR/Ethics: Responsible purchasing dilemmas, impact estimation; guided trade-offs.
Quiz, Serious Game, or Escape Game?
The serious game simulates a comprehensive system (economic loops, resource management). The escape game focuses on collaborative problem-solving under constraints using logical gates. Quizzes are still useful for point-in-time memorization, but escape games anchor knowledge in contextualized missions involving decision-making and storytelling.
Digitalizable Puzzle Mechanics
- Codes: Numeric Keypad/Input field
- Association/Sorting: Matching, Drag & Drop, Ordered Quiz
- Exploration: Clickable zones, Decor interaction
- Estimation: Slider
- Time Pressure: Countdown
- Variability: Random, Switch, Sequence, Variable Media
- Immersion: Fullscreen Video, Foreground, Sound (fade-in/spatial), Emotion/Animation/Eye Contact, 360° environments
Benefits and ROI of Training Escape Games
Engagement and Motivation: The Flow Effect
Progressive difficulty, tiered clues, and time constraints create an optimal challenge. Exploration and surprises (random outcomes, branching) stimulate curiosity. Intrinsic motivation is driven by mission purpose, team autonomy, and instant feedback. Research confirms that the flow state supports learning in gamified settings (Hamari et al., 2016).
Memory and Transfer: Learning by Doing
Participants solve problems in realistic settings with visual and auditory cues, enhancing contextual encoding and long-term memory. Immediate corrections and guided debriefing support consolidation; replayability enables smart spaced repetition (via Random and Variable Media). The “testing effect” shows that frequent assessment boosts retention (Roediger & Karpicke, 2006). A systematic review of educational escape rooms highlights collaboration and problem-solving as key learning accelerators (Veldkamp et al., 2020).
Soft Skills and Team Dynamics
Communication, listening, leadership, decision-making under stress are revealed through action: who coordinates, rephrases, prioritizes? In synchronous sessions, facilitators observe and highlight behaviors; in asynchronous sessions, analysis of user paths (time, attempts, hint requests) illuminates support needs. Discover more gamified formats on our pedagogical escape games page.
Measurement, Data, and Monitoring
Overall and skill-based scores, success thresholds, completion/success rates, time and attempts are tracked via SCORM in the LMS. Contextual feedback can be configured depending on performance (differentiated responses per scores and flags). Deployed via VTS Perform, escape games feed your L&D dashboards, aiding in budget decisions and ROI demonstration.
Accessibility, Inclusiveness, and Language Options
Activable subtitles, text-to-speech in multiple languages, zoomable visuals, optional hints, puzzle variants to avoid dead-ends; language-based conditions to publish localized versions without rebuilding the scenario. These elements support internal compliance and equitable access.
ROI: Controlled Costs, Industrialization, and Maintenance
The no-code approach of VTS Editor allows a fast prototype. Puzzle patterns become reusable blocks (Function Mode Group + Function Call). Variables and variable media limit duplication. SCORM export and accelerated translation simplify updates. You can continuously fine-tune difficulty, hints, and duration—right where the impact is strongest.
Designing an Effective Pedagogical Escape Room
Define Objectives and KPIs
Clarify target skills (technical, behavioral, cognitive) and success criteria: minimum score, maximum time, tolerated critical errors, target badges. For L&D KPIs, track completion, satisfaction/NPS, 30-day perceived transfer, and ideally a business metric (incident reduction, sales conversion). Configure Score/Check Score, Counter (attempts), Countdown (time), Progress (success/completion), and Badges.
Scenario and Narrative: From Brief to Storyboard
Use a four-step structure: introduction (context, goals, instructions), rising tension (more puzzles and decisions), climax (final gate, critical code), resolution/debrief (feedback, resource links). Plan clues in levels: initially subtle, then more direct, finally the solution for a penalty. Provide « success/failure » paths and crisis exit shortcuts to avoid frustration.
Translate into VTS Editor Blocks
- Powerful Brief: Text Animation or Message for objective, Slideshow/Video for context, Sound for ambience, Foreground for alerts.
- Acting: Speak + Emotion/Eye/Character Animation for realistic dialogues.
- Exploration: Clickable zones, Decor Interaction, Media in Decor to hide clues.
- Logic: Flags/Check Flags for logical gates, Switch/Sequence for flow control, Wait for pacing.
- Closure: Recap, Progress (success/failure), Message for personalized debrief, Badge to celebrate.
Puzzle Design: Variety, Progression, Fairness
Mix mechanics to stimulate different strategies (concept association, categorization, calculation, observation, estimation, validation). Provide a quick « early win, » ramp up complexity, adjust time pressure. Avoid dead ends: tiered clues, last-resort solution with penalty, return to last Checkpoint/Back. Test early, measure (avg. time, errors, hints, dropouts), iterate in short loops.
Technical Orchestration Without Coding
- Readable Graph: Group by puzzle, name blocks and scenes clearly, harmonize colors.
- Status and Conditions: Track progress with Flags; route via Switch per step; sequence via Sequence; Checkpoint/Back for smooth replays.
- Variables (Integral Plan): Store user answers, control visibility of a clue or zone, activate Variable Media to vary without duplication.
- Reusability: Encapsulate a pattern (instruction + interaction + validation + feedback) into a Function Mode Group; reuse via Function Call.
Useful Gamification and Feedback
Tie scores to learning: fewer hints or attempts = more points; critical errors = penalties. Badges mark milestones (time mastery, perfect compliance, no hints). Feedback must be actionable: Message and integrated comments in Quizzes for immediate return; final debrief personalized based on flags and scores, with resource links for further learning.
Execution Quality and Deployment
Before rollout, optimize UX: clear and visual instructions, legible clues, large interactive zones, multilingual subtitles and TTS, zoomable visuals. Optimize media (videos at 1280×720, audio fades, spatial sound when relevant). For publishing, configure project settings (progress bar, overall time limit, language), use Language Condition for localized versions, export in SCORM. For advanced deployment and tracking, see VTS Perform.
Next Concrete Steps
- Frame 1 or 2 priority skills and their KPIs (score, time, critical errors).
- Write a simple 3–4 act storyboard; plan 3 to 5 varied puzzles with tiered clues.
- Prototype without code in VTS Editor: interactions, logic, and media; include Variables and Variable Media for replayability.
- Test with a small internal group, iterate quickly, export via SCORM, and track your results.
Ready to accelerate? Request a VTS Editor demo or explore our pedagogical escape games. To discover our solutions and services, visit the Revolutionize your E-Learning strategy with Serious Factory page.
Explore our exclusive resource on educational escape games: learn how to define, design, and deploy your programs to maximize the impact of your training.
👉 Access the content