Business Games in Professional Training: Definition and Key Benefits
Business Games in professional training are interactive learning experiences where the learner makes decisions in situations that closely resemble real life: leading a team, managing a budget, responding to a demanding customer, sorting weak signals in cybersecurity, applying a quality procedure. Unlike generalized serious games, these business-oriented games target performance and concrete indicators (objectives, compliance, incidents avoided). Unlike simple simulations, they combine storytelling, game mechanics (scores, badges, challenges), and targeted feedback to accelerate skill acquisition.
Why It’s a Relevant Choice Today
Training today must combine a blend of in-class/remote learning, develop soft skills, and adapt to more complex environments (regulations, security, digital). The time required to master a subject is shrinking: managers and teams can’t afford weeks of practice. Business Games fulfill this need through active learning, immediate feedback, and replayable paths. With a no-code authoring tool like VTS Editor, these experiences can be built without technical or graphic skills and are easily integrated into your ecosystem (SCORM/LMS).
Proven Effectiveness
Numerous studies confirm the value of business games for training. A meta-analysis shows that serious games improve both learning and motivation compared to passive formats (Wouters et al., Journal of Educational Psychology). Another concludes that simulations/management games improve learning outcomes compared to traditional methods (Sitzmann, Personnel Psychology). On the gamification side, research highlights positive effects on engagement, provided the game mechanics are aligned with learning objectives (Hamari, Koivisto & Sarsa, HICSS). Finally, spaced repetition improves retention and on-the-job transfer (Cepeda et al., Psychological Bulletin).
Maximizing Engagement and Retention with Business Games
Active Learning in Business Games
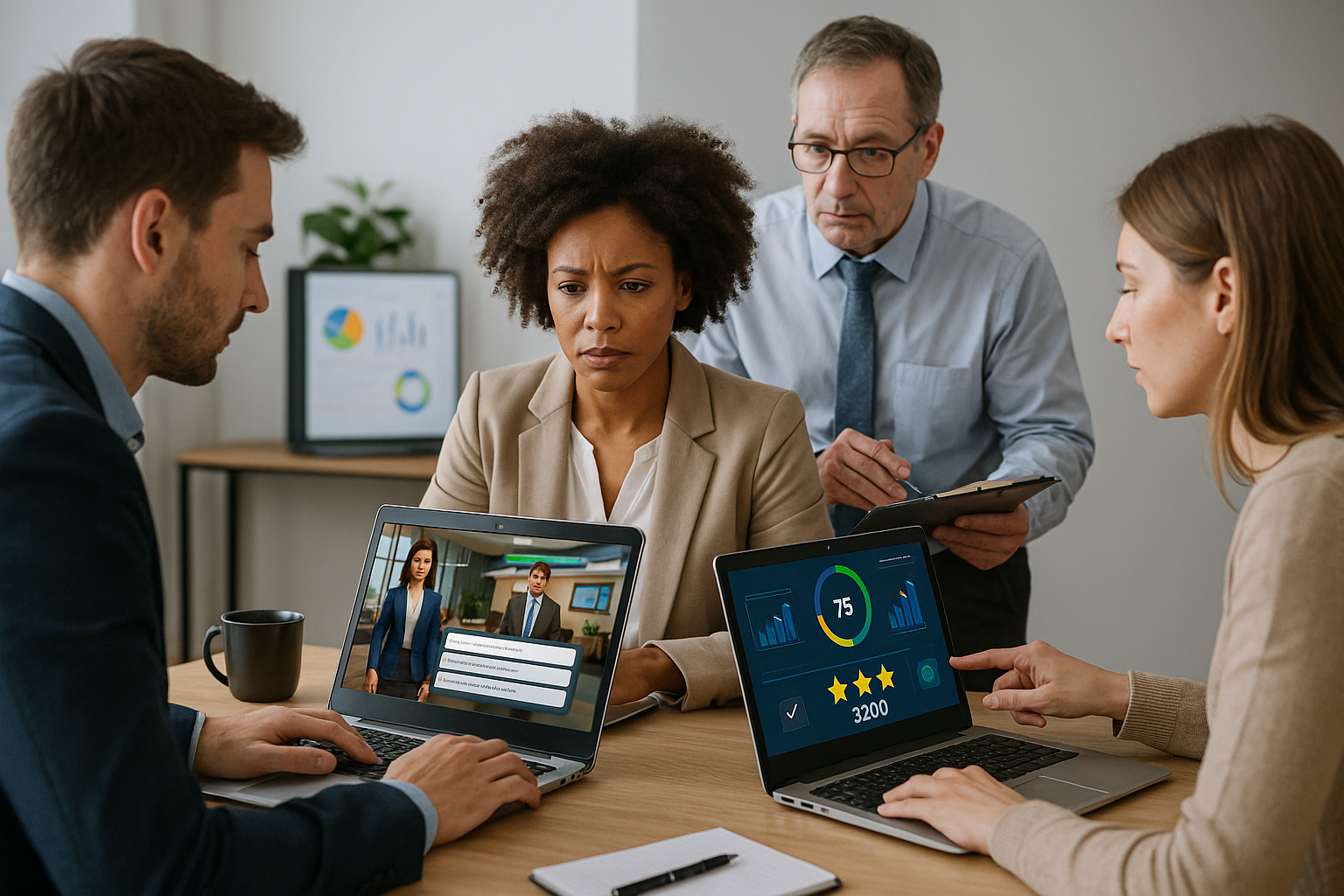
The decision–action–consequence–debrief loop is the core of effective business games. The learner analyzes context, makes a choice, observes a credible reaction, then understands why that choice led to that result. In VTS Editor, this translates into dialogue (block Speak), decisions (block Speech Choices), and visible consequences (block Emotion, Character Animation, Sound, Scene Media). Concrete examples: a performance review, a negotiation, a project meeting. You learn because you feel, understand, and can immediately try again.
Purposeful Gamification in Business Simulations
Gamification should guide, not distract. The skill-based score (block Score) objectifies progress without reducing the exercise to “points.” The Score Check block can unlock a level or provide help if a threshold isn’t met. Badges (block Badge) mark progress (“Savvy Negotiator,” “Zero Non-Compliance”). Instant, contextual feedback (block Message or reused Speak) explains the impact of a choice and offers alternatives. A Countdown simulates real-world pressure (e.g., security alert in 90 seconds) without preventing learning.
Accessible Instructional Realism and Immersion
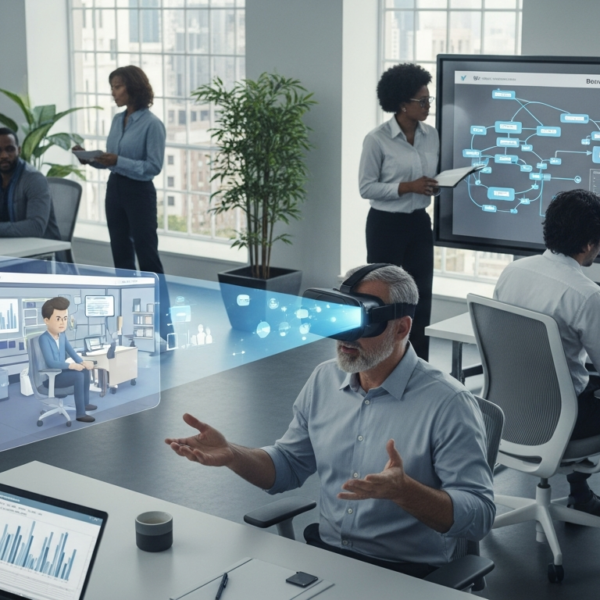
Credible characters, professional settings, integrated documents (Scene Media), synthetic voices, and ambient sound make the situation more authentic. A good habit: alternate between information and exploration. For example, a Speak block to set the stage, a Slideshow to visualize a process, a short Video, then a decision via Speech Choices or Clickable Zones requires the learner to apply what they just saw.
Non-Linear, Replayable Learning Paths
A well-designed Business Game opens up useful, clear pathways. You can vary scenarios using Random, route to scenes by variable (Switch), or chain together targeted exercises (Sequence). Flags and Flag Checks record key decisions to provide advanced content. The Reset block cleanly replays a quiz; a Counter limits attempts before guided help is offered. Result: a dynamic, motivating, and controlled experience.
Accessibility and Inclusivity at the Core
L&D teams aim for both performance and accessibility. VTS Editor supports multiple access modes: text-to-speech, subtitles, zoomable images (in Quiz/Message blocks), appropriate contrast, clear navigation. For international deployments, you can change language without duplicating logic (Language Condition). From desktop to mobile, the experience remains smooth by optimizing media file sizes and offering clear progress bars and concise instructions.
Key Skills: From Soft to Hard, Assessed by Business Games
Soft Skills in Business Games
Communication, leadership, negotiation, conflict management are developed through guided practice. Example: a management game where the learner prepares feedback for a struggling employee. Decisions are made with Speech Choices; emotions and body language (Emotion, Character Animation) make relational effects visible; the Gaze block aligns eye contact to make the interaction credible. Competency scoring (Score) and targeted debriefs (Message/Speak) explain how to improve, from guided path to autonomous challenge.
Hard Skills, Safety, and Compliance
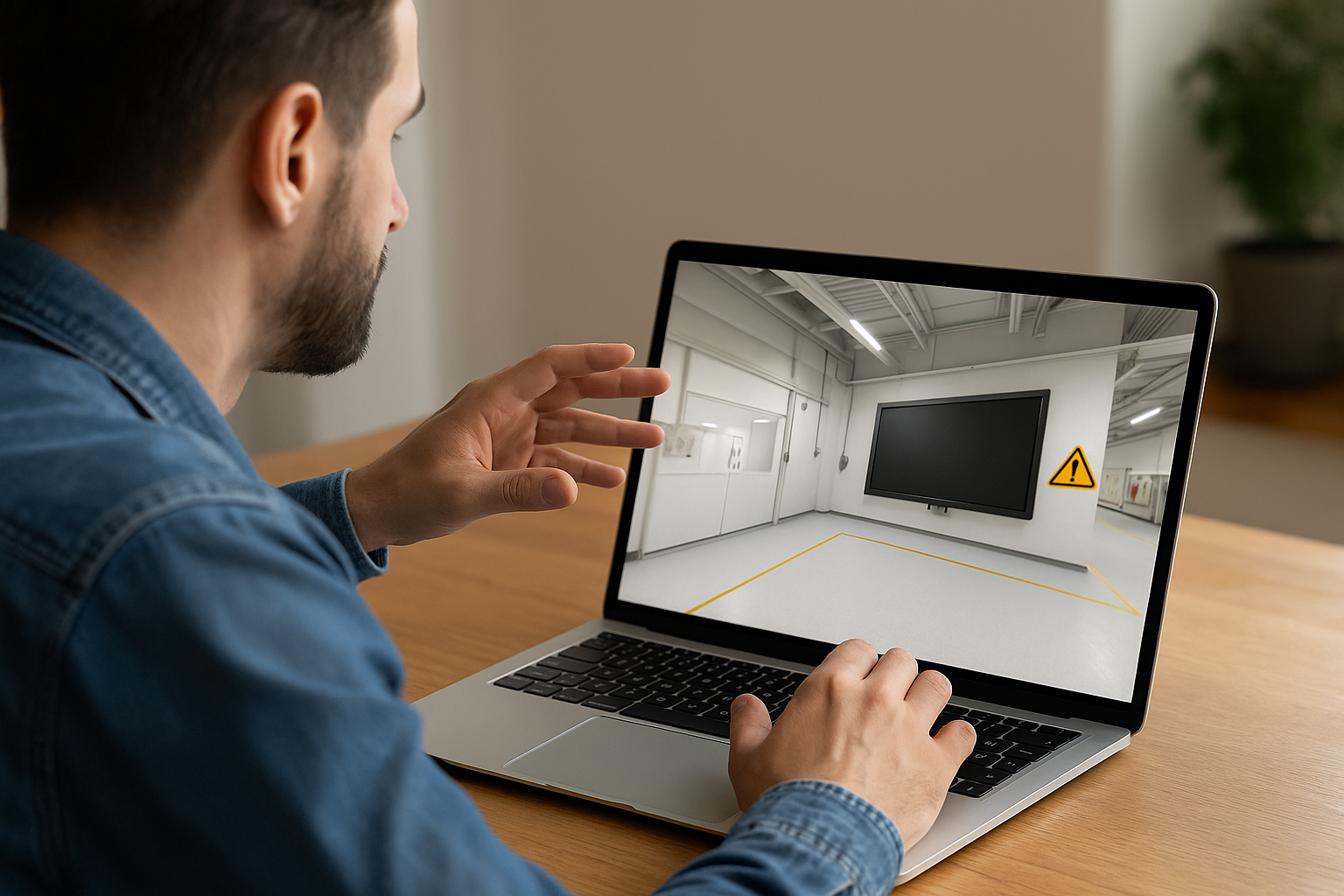
Procedures, safety, quality, and cybersecurity require rigor and repetition. A common progression: a Slideshow or Video to show a procedure, followed by Quizzes (single/multiple choice, sort order), a True/False to validate rules, and Matchings or Drag & Drop to handle vocabulary and rules. For cybersecurity, a phishing scenario combines Clickable Zones, Countdown, and a debrief that compares the decision to internal policy.
Safe-to-Fail: The Right to Make Mistakes Without Stress
A major advantage of business simulations: making failure instructive, not punitive. An error triggers a simulated consequence, followed by feedback highlighting the mistake and suggesting a plan B. Reset restarts the exercise, Counter limits attempts before providing help, and Flags activate a resource after repeated errors. This reduces stress while maintaining high standards.
Measurement, KPIs, and Useful Analytics
Skill scores and thresholds (Score, Score Check) guide progression. The Progression block defines an advancement percentage, completion and success status, and sends data to the LMS. SCORM export ensures compatibility. For specific integrations (IS, forms, dashboards), Web Request sends or receives data. With VTS Perform, you can track completions, active time, skill scores, attempts, and learning paths, then link these data points to field indicators (incidents, quality, satisfaction) to document ROI.
Operational Transfer and Anchoring
A systematic debrief anchors the skill: “Why does this option work better in this context?” Action plans use direct access to checklists or procedures (Open Resource). Consolidation is reinforced with regular microcapsules: a review Slideshow, a short Tips Video, a flash Quiz. Spaced repetition maintains retention without monopolizing the calendar.
Deploying Business Games at Scale Without Technical Skills
Choosing the Right No-Code Authoring Tool
To industrialize production, a no-code tool like VTS Editor is a strategic ally. Its block-based interface allows instructional designers and L&D/HR managers to create gamified e-learning modules without coding. A library of interactions (dialogues, quizzes, clickable zones), 3D avatars, emotions, text-to-speech, SCORM export, and multilingual support cover all needs. Logic (using Flags, Flag Checks, Random, Switch, Sequence, Counter, Language Condition) enables adaptive paths. Instant preview and AI-assisted support (text, blocks, translation) fast-track development.
Answers to L&D and HR Key Questions
- Production time: from a few days for a pilot to a few weeks for a multilingual course, thanks to reusable templates, scenes, and features.
- Budget: variable depending on the number of cases and media; savings via scalability, fewer incidents, and faster time‑to‑competency.
- IS integration: SCORM publication to LMS, SSO if available, specific connections via Web Request.
- Quality & accessibility: voice/subtitles/text, testing on multiple devices, optimized media, structured instructional review.
Simple Design Method
Start with a clear framework (audience, situations, target skills, success criteria, time/device/language constraints). Script the key decisions, define feedback, and plan progression from guided to autonomous. Prototyping: create a playable “vertical slice” with decisions, feedback, and metrics. Test instruction clarity, cognitive load, and feedback relevance. Rapid improvement via A/B testing (feedback type, success thresholds, duration, randomness level) on content and mechanics (scoring, branches).
Easy-to-Apply Best Practices
- Immediate, specific, actionable feedback: link the consequence to the choice and offer a support resource.
- Progressive difficulty: from guided to challenging, with checkpoints (Score Check) and conditional help (Flags).
- Coherent branches: clear structure, limited and documented paths for easier maintenance.
- Accessibility: enable subtitles, provide voice-over, ensure proper contrast and navigation, adapt via Language Condition.
Smooth Integration and Distribution
Ideally distribute via your LMS (SCORM), SSO if possible. On multiple devices, test display of key elements (progress bar, buttons, resources). In multiple languages, duplicate only the text/media layer without multiplying logic; centralize translations and test text length/alignment. On IT side, validate network flows in advance to avoid blockages.
Measure ROI and Continuously Improve
Define readable indicators: adoption (registrations, launches, completions), engagement (active time, replayability), performance (skill scores, attempts before success, progression), field impact (incidents, quality, productivity, satisfaction). Method: combine A/B tests, pre/post comparisons, and training-performance correlations. The optimization loop is continuous: collect, analyze, improve, document — with the support of VTS Perform for tracking.
Take Action: Launch a Quick Pilot Business Game in Training
From Concept to Measurable Rollout
Start with a high-stakes target, clear KPIs, and a playable vertical slice, quickly produced with a no-code authoring tool. Test on a small sample, adjust quickly, then roll out at scale once value is proven. Leverage reusable templates, a skill-based feedback grid, and scenario archetypes. Business Games in professional training turn learning time into training time, bring training closer to field realities, and enable precise skill-level assessment.
Go Further
- Discover the solution: Business Games
- Create your simulations: VTS Editor
- Deploy and measure: VTS Perform
- Request a personalized demo: Request a demonstration
Dive into our in-depth resource: learn how to frame, design, and deploy your Business Games to maximize impact.
👉 Explore the content